Guest Post for International Anti-Street Harassment Week
By Girija Borker
Why do women in India choose to attend lower ranked colleges?
Is it because women have lower high school test scores? No.
Is it because of street harassment? YES.
Women studying in Delhi University (DU), one of the top universities in India, choose lower ranked colleges than men with the same high school test scores. This is despite the fact that women score higher on national high school exams than men. And this is true even for the smartest and the most ambitious women. My research aims to understand why women are making these choices and whether it is because women trade-off quality of education for safety from harassment.
DU is composed of 77 colleges and the colleges are spread across Delhi. The colleges vary in quality, with each college having its own campus, staff and classes. Undergraduate admissions in DU are centralized and primarily based on students’ high school test scores. I surveyed over 4,000 students at DU to collect information on students’ daily travel route, travel mode, their high school scores and exposure to street harassment. At DU, most students live with their parents and travel to college every day, predominantly by public transport. In my sample, over 70% of students live at home and of these around 80% use public transport to travel to college every day. Most women I surveyed have experienced some form of street harassment – 63% of women have experienced unwanted staring, 50% have received inappropriate comments, 27% have been touched inappropriately and 25% have been followed.
To determine how the risk of harassment during travel affects college choice, I combine safety data with information on students’ chosen travel route and alternative travel routes available. Safety data comes from SafetiPin, a map-based mobile application that allows users to characterize the safety of an area. Information on harassment by travel mode comes from Safecity, a mobile application that lets women share their stories of harassment in urban public spaces. I used Google Maps to map the route options available to each student for their travel to college every day.
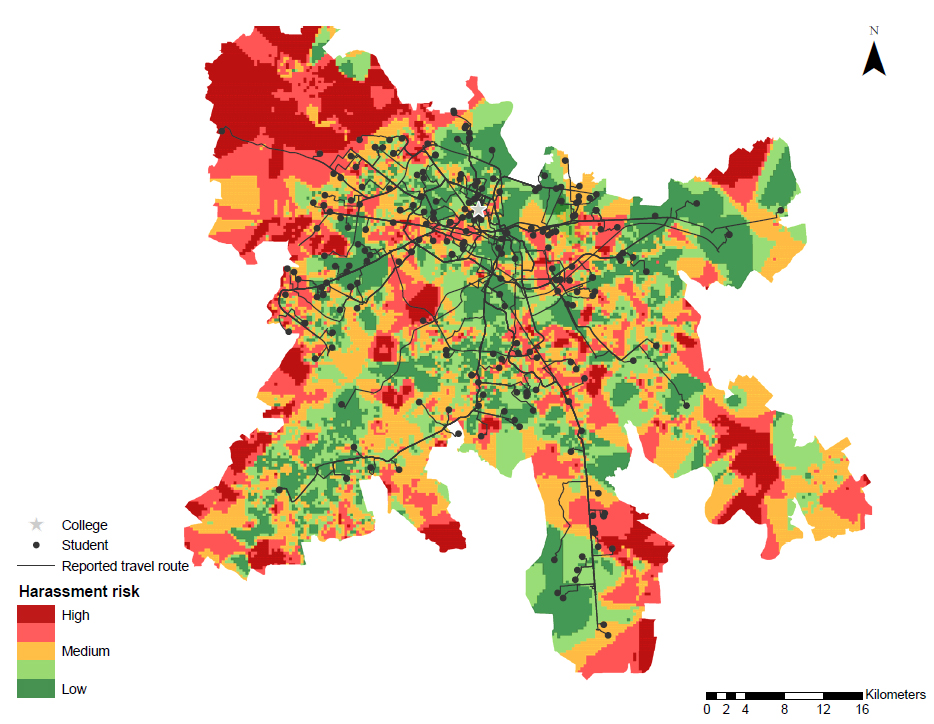
This is the first study to assess the effects of street harassment on women’s college choice. The study highlights the degree to which the threat of street harassment holds back promising young women, even at a prestigious university in a modern city. The findings speak to the long-term consequences of everyday harassment – perpetuating gender inequality in education. Policy makers must realize that affirmative action for women is not enough unless we transform public spaces into enabling environments that are accessible to all.
