Eve Aronson, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, SSH Blog Correspondent
Have you heard of the Dutch Myth of Tolerance? It’s not a myth in the mythical sense, and it’s not a fairytale, though it does sound admittedly magical.
Since the 17th century, the Netherlands has been a smorgasbord of races, ethnicities and religions and has continuously championed itself on what are known as “pillars” of tolerance.
The Dutch Myth of Tolerance is reflective of the disintegration of these pillars towards what has become an increasingly harsh critique of the narrative of ‘acceptance and multiculturalism’ in the Netherlands (or the lack thereof).
At first, the presence of this myth throughout my research was subtle. People told me about their experiences of street harassment and may have thrown in some (racially) identifying characteristics of their harassers. But after several months, it became evident that a more solid smokescreen lurked, and that the notion of Dutch pluralism and tolerance was not always as strong as it presented itself to be.
When people talk about street harassment in Amsterdam, it is not uncommon to highlight the race or ethnicity of one’s harassers, particularly if they are of Moroccan or Turkish decent, two of the largest minority populations in the Netherlands. Often times, the harasser is also tied to a particular neighborhood. For example, one person I talked to said: “In my experience, harassment was worse in neighborhoods with a lot of immigrants from cultures…Moroccans for example.” Another echoed: “A lot of catcalling, primarily from members of black communities”.
A report released in March of this year by the city of Amsterdam also highlighted particular minority-populated neighborhoods and communities as being more affected by street harassment, which arguably worked to further emphasize the link between street harassment and race or ethnicity.
Many of you might also recall the October 2014 video of a woman walking through the streets of New York in the US. The video heavily criticized for selectively showing a disproportionate number of men of color harassing the (white) woman in the video. Emphasizing connections between street harassment, race and location is not only completely inaccurate; it also strips accountability from a significant proportion of harassers who fall outside of these stereotypes and who are harassing women in Amsterdam just as often.
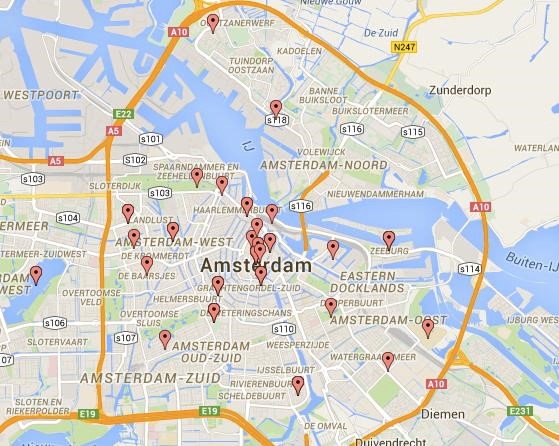
Below is a map of locations tagged by 48 respondents of a recent street harassment survey that I conducted in Amsterdam. Take a good look at where the majority of incidents are reported:
The majority of the geotagged incidents were reported in the center of the city, mostly around touristy areas and not in areas of the city known to have large minority populations (Biljmer, Zuid-Oost and Oost, for example). What this data does then, is encourage a revisiting of stereotypes of street harassment in Amsterdam, albeit from a purely geographic perspective. And this is just a start. The more stereotypes are checked—particularly using visual tools and visualizations—the more people are realizing that street harassment extends beyond race, ethnicity and geographical area.
What kind of impact does this have on the ground? Understanding street harassment as part of broader power structures does not mean that everyone gets this memo, and in this vein, individuals’ lived experiences are critical to take into account. But without denying individual experiences with street harassment, it is important to underline the implications of making generalized statements about races or communities.
Starting up a Hollaback! in Amsterdam is one way to work towards exposing exactly what happens on the ground and where. Geotagging experiences of street harassment not only confronts the Dutch Myth of Tolerance but it also provides an important starting point for conversations about street harassment and race in the Netherlands. Coupled with other awareness-raising initiatives and campaigns, addressing racial stereotyping in conversations about street harassment through such visual tools also encourages a look at street harassment through a much broader lens—one that unfortunately does not make the fight against street harassment easier but who said this was going to be easy? Ultimately, what taking a more comprehensive approach to street harassment does, is it makes the work more strategic and more effective in the long run.
You can find the full analysis of the Amsterdam survey results here or by contacting Eve at evearonson@gmail.com. Follow Eve and Hollaback! Amsterdam on Twitter at @evearonson and @iHollaback_AMS and show your support by liking Hollaback! Amsterdam’s Facebook page here.